KubeSphere 是一个以 Kubernetes 为内核的云原生分布式操作系统,它的架构可以非常方便地使第三方应用与云原生生态组件进行即插即用(plug-and-play)的集成,支持云原生应用在多云与多集群的统一分发和运维管理。KubeSphere 是一个 Kuberetes 的人性化 UI,但又不仅限于一个 UI。本文记录了笔者对 KubeSphere 的初步探索。
准备工作
笔者拥有一个包含 11 个节点的集群,这些节点(私网 IP 地址为 192.168.23.160~192.168.23.170)相互之间可以免密登录,且均不具备公网 IP。
在本机(macOS 10.15)通过 ssh 登录到节点 ubuntu 上获取各节点信息:
k8s@ubuntu:~$ k get no -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
ubuntu Ready control-plane,master 27d v1.22.2 192.168.23.160 <none> Ubuntu 18.04.5 LTS 4.15.0-112-generic docker://20.10.9
worker-large-2 Ready <none> 27d v1.22.2 192.168.23.161 <none> Ubuntu 18.04.5 LTS 4.15.0-112-generic docker://20.10.9
worker-large-3 Ready <none> 27d v1.22.2 192.168.23.162 <none> Ubuntu 18.04.5 LTS 4.15.0-112-generic docker://20.10.9
worker-medium-1 Ready <none> 27d v1.22.2 192.168.23.163 <none> Ubuntu 18.04.5 LTS 4.15.0-112-generic docker://20.10.9
worker-medium-2 Ready <none> 27d v1.22.2 192.168.23.164 <none> Ubuntu 18.04.5 LTS 4.15.0-112-generic docker://20.10.9
worker-medium-3 Ready <none> 27d v1.22.2 192.168.23.165 <none> Ubuntu 18.04.5 LTS 4.15.0-112-generic docker://20.10.9
worker-medium-4 Ready <none> 27d v1.22.2 192.168.23.166 <none> Ubuntu 18.04.5 LTS 4.15.0-112-generic docker://20.10.9
worker-small-1 Ready <none> 27d v1.22.2 192.168.23.167 <none> Ubuntu 18.04.5 LTS 4.15.0-112-generic docker://20.10.9
worker-small-2 Ready <none> 27d v1.22.2 192.168.23.168 <none> Ubuntu 18.04.5 LTS 4.15.0-112-generic docker://20.10.9
worker-small-3 Ready <none> 27d v1.22.2 192.168.23.169 <none> Ubuntu 18.04.5 LTS 4.15.0-112-generic docker://20.10.9
worker-small-4 Ready <none> 27d v1.22.2 192.168.23.170 <none> Ubuntu 18.04.5 LTS 4.15.0-112-generic docker://20.10.9
在正式安装 KubeSphere 1 之前,需要做一些准备工作。 首先,KubeSphere 需要一个集群级别的 nfs 服务器可用,并且要求基于此配置一个默认存储类(default StorageClass)。 所谓默认存储类,即当我们想要创建 PVC 申请 PV 时,如果不指定存储类别(如下面的示例所示),那么 Kubernetes 会立即通过默认存储类为我们创建一个与 PVC 请求一致的 PV 出来,并与之绑定。 也就是说,配置了默认存储类之后,我们就无需手动创建 PV 了。
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: pvc
namespace: dev
spec:
accessModes:
selector:
storageClassName: # 不指定存储类别,本行不写
resources:
requests:
storage: 5Gi
我们通过如下资源清单配置动态供应的默认存储类,读者可以直接 copy 下面的配置,但是需要修改 nfs server 的内网 IP 和共享目录:
# default-sc.yaml
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: nfs-storage # 默认存储类的名称
annotations:
storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "true"
provisioner: k8s-sigs.io/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner
parameters:
archiveOnDelete: "true" # 删除 pv 的时候,pv 的内容是否要备份
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner
labels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
namespace: default # 放在默认命名空间下。当然,也可以放在别的空间下。后续的对象要与该 provisioner 放在一个空间下
spec:
replicas: 1
strategy:
type: Recreate
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
spec:
serviceAccountName: nfs-client-provisioner
containers:
- name: nfs-client-provisioner
image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/lfy_k8s_images/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner:v4.0.2
volumeMounts:
- name: nfs-client-root
mountPath: /persistentvolumes
env:
- name: PROVISIONER_NAME
value: k8s-sigs.io/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner
- name: NFS_SERVER
value: 192.168.23.160 # 将节点 ubuntu 做成 nfs 服务器
- name: NFS_PATH
value: /srv/nfs4/ks # nfs 服务器共享的目录
volumes:
- name: nfs-client-root
nfs:
server: 192.168.23.160
path: /srv/nfs4/ks
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner
namespace: default
---
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner-runner
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["nodes"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["persistentvolumes"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "delete"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["persistentvolumeclaims"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "update"]
- apiGroups: ["storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["storageclasses"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["events"]
verbs: ["create", "update", "patch"]
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: run-nfs-client-provisioner
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: nfs-client-provisioner
namespace: default
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: nfs-client-provisioner-runner
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner
namespace: default
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["endpoints"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch"]
---
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner
namespace: default
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: nfs-client-provisioner
namespace: default
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
查看上述资源对象是否被成功创建:
k8s@ubuntu:~/learn-k8s/16-kubesphere$ k get sc -A
NAME PROVISIONER RECLAIMPOLICY VOLUMEBINDINGMODE ALLOWVOLUMEEXPANSION AGE
nfs-storage (default) k8s-sigs.io/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner Delete Immediate false 17h
接下来,我们创建一个 PVC 来测试默认存储类是否可以正常工作:
# test-default-sc.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: pvc1
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
可以发现,一切正常运行:
k8s@ubuntu:~/learn-k8s/16-kubesphere$ k apply -f test-default-sc.yaml
persistentvolumeclaim/pvc1 created
# 默认存储类为我们立即创建了一个 PV 并与 PVC 绑定
k8s@ubuntu:~/learn-k8s/16-kubesphere$ k get pv
NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGE
pvc-dadcc223-a827-45e4-a5f6-c52fc1658969 1Gi RWX Delete Bound default/pvc1 nfs-storage 3s
k8s@ubuntu:~/learn-k8s/16-kubesphere$ k get pvc
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
pvc1 Bound pvc-dadcc223-a827-45e4-a5f6-c52fc1658969 1Gi RWX nfs-storage 10s
# 删除 PVC 之后,与之绑定的 PV 也会被删除
k8s@ubuntu:~/learn-k8s/16-kubesphere$ k delete -f test-default-sc.yaml
persistentvolumeclaim "pvc1" deleted
k8s@ubuntu:~/learn-k8s/16-kubesphere$ k get pv
No resources found
k8s@ubuntu:~/learn-k8s/16-kubesphere$ k get pvc
No resources found in default namespace.
我们还需要安装 Metric Server(https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/metrics-server),此处不再展示安装细节。安装成功之后,可以通过 top 命令查看节点或 Pod 的资源消耗情况:
k8s@ubuntu:~$ k top nodes
NAME CPU(cores) CPU% MEMORY(bytes) MEMORY%
ubuntu 386m 2% 3776Mi 12%
worker-large-2 247m 1% 5269Mi 16%
worker-large-3 158m 0% 5166Mi 16%
worker-medium-1 100m 1% 3290Mi 22%
worker-medium-2 115m 1% 1499Mi 10%
worker-medium-3 206m 2% 2565Mi 17%
worker-medium-4 116m 1% 2785Mi 18%
worker-small-1 100m 2% 1316Mi 16%
worker-small-2 96m 2% 1312Mi 16%
worker-small-3 85m 2% 1246Mi 18%
worker-small-4 107m 2% 1351Mi 19%
k8s@ubuntu:~/learn-k8s/16-kubesphere$ k top po -A
NAMESPACE NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
default nfs-client-provisioner-645fcf5574-75jvn 2m 9Mi
ingress-nginx ingress-nginx-controller-69bb54574d-fnlmp 5m 243Mi
kube-system coredns-7f6cbbb7b8-6v7ll 2m 16Mi
kube-system coredns-7f6cbbb7b8-f8wrp 2m 16Mi
kube-system etcd-ubuntu 30m 53Mi
kube-system kube-apiserver-ubuntu 85m 328Mi
kube-system kube-controller-manager-ubuntu 16m 60Mi
kube-system kube-flannel-ds-7mffj 3m 11Mi
kube-system kube-flannel-ds-cfb8h 3m 14Mi
kube-system kube-flannel-ds-d576s 4m 20Mi
kube-system kube-flannel-ds-hrkhs 4m 12Mi
kube-system kube-flannel-ds-hwwwb 3m 14Mi
kube-system kube-flannel-ds-kgv7t 3m 12Mi
kube-system kube-flannel-ds-lng6z 4m 15Mi
kube-system kube-flannel-ds-nhgfr 4m 19Mi
kube-system kube-flannel-ds-tj9ks 3m 12Mi
kube-system kube-flannel-ds-tq96j 3m 14Mi
kube-system kube-flannel-ds-zxt7t 5m 19Mi
kube-system kube-proxy-8vg69 14m 18Mi
kube-system kube-proxy-bz7cx 8m 18Mi
kube-system kube-proxy-cbdx8 14m 25Mi
kube-system kube-proxy-dg8x5 18m 23Mi
kube-system kube-proxy-f8hkk 13m 15Mi
kube-system kube-proxy-fcxg6 13m 14Mi
kube-system kube-proxy-qllwh 21m 18Mi
kube-system kube-proxy-srndp 14m 24Mi
kube-system kube-proxy-x6vcp 13m 14Mi
kube-system kube-proxy-xkt2j 16m 14Mi
kube-system kube-proxy-xrzg4 8m 18Mi
kube-system kube-scheduler-ubuntu 4m 24Mi
kube-system metrics-server-74774dcf94-4cgvj 5m 24Mi
kubernetes-dashboard dashboard-metrics-scraper-c45b7869d-nvg8x 1m 12Mi
kubernetes-dashboard kubernetes-dashboard-576cb95f94-fxgz4 1m 17Mi
现在,我们安装 KubeSphere。具体安装步骤请参考官方文档 2,此处不再展示安装细节。如果一切顺利,应当可以看到如下内容:
k8s@ubuntu:~/learn-k8s/16-kubesphere$ k get po -A | grep kubesphere
kubesphere-controls-system default-http-backend-5bf68ff9b8-8hv4s 1/1 Running 0 25m
kubesphere-controls-system kubectl-admin-6dbcb94855-lzxvg 1/1 Running 0 17m
kubesphere-devops-system devops-27276750--1-zc9lq 0/1 Completed 0 6m32s
kubesphere-devops-system devops-apiserver-77484746cb-n7h57 1/1 Running 0 20m
kubesphere-devops-system devops-controller-7dc9554b48-wj87r 1/1 Running 0 20m
kubesphere-devops-system devops-jenkins-5d744f66b9-25hq7 1/1 Running 2 (9m34s ago) 20m
kubesphere-devops-system s2ioperator-0 1/1 Running 0 20m
kubesphere-logging-system elasticsearch-logging-data-0 1/1 Running 0 26m
kubesphere-logging-system elasticsearch-logging-data-1 1/1 Running 0 23m
kubesphere-logging-system elasticsearch-logging-data-2 1/1 Running 0 22m
kubesphere-logging-system elasticsearch-logging-discovery-0 1/1 Running 0 26m
kubesphere-logging-system elasticsearch-logging-discovery-1 1/1 Running 0 23m
kubesphere-logging-system elasticsearch-logging-discovery-2 1/1 Running 0 22m
kubesphere-logging-system fluent-bit-5fh6d 1/1 Running 0 24m
kubesphere-logging-system fluent-bit-8bvs6 1/1 Running 0 24m
kubesphere-logging-system fluent-bit-98nnr 1/1 Running 0 24m
kubesphere-logging-system fluent-bit-9snp7 1/1 Running 0 24m
kubesphere-logging-system fluent-bit-fsfxt 1/1 Running 0 24m
kubesphere-logging-system fluent-bit-g25ml 1/1 Running 0 24m
kubesphere-logging-system fluent-bit-jq64v 1/1 Running 0 24m
kubesphere-logging-system fluent-bit-l7vlq 1/1 Running 0 24m
kubesphere-logging-system fluent-bit-qjrvn 1/1 Running 0 24m
kubesphere-logging-system fluent-bit-rk2mw 1/1 Running 0 24m
kubesphere-logging-system fluent-bit-tdgk6 1/1 Running 0 24m
kubesphere-logging-system fluentbit-operator-745bf5559f-4cf6f 1/1 Running 0 26m
kubesphere-logging-system ks-events-exporter-59d48f6777-wwmfg 2/2 Running 0 21m
kubesphere-logging-system ks-events-operator-5944645757-9dlxz 1/1 Running 0 21m
kubesphere-logging-system ks-events-ruler-575669b4-nkt9g 2/2 Running 0 21m
kubesphere-logging-system ks-events-ruler-575669b4-xhzfr 2/2 Running 0 21m
kubesphere-logging-system kube-auditing-operator-84857bf967-6bv85 1/1 Running 0 22m
kubesphere-logging-system kube-auditing-webhook-deploy-64cfb8c9f8-6nftf 1/1 Running 0 22m
kubesphere-logging-system kube-auditing-webhook-deploy-64cfb8c9f8-8lkhn 1/1 Running 0 22m
kubesphere-logging-system logsidecar-injector-deploy-5fb6fdc6dd-4sfv9 2/2 Running 0 21m
kubesphere-logging-system logsidecar-injector-deploy-5fb6fdc6dd-q4l4z 2/2 Running 0 21m
kubesphere-monitoring-system alertmanager-main-0 2/2 Running 0 19m
kubesphere-monitoring-system alertmanager-main-1 2/2 Running 0 18m
kubesphere-monitoring-system alertmanager-main-2 2/2 Running 0 18m
kubesphere-monitoring-system kube-state-metrics-5547ddd4cc-7zwlq 3/3 Running 0 19m
kubesphere-monitoring-system node-exporter-42hh4 2/2 Running 0 19m
kubesphere-monitoring-system node-exporter-5cvwl 2/2 Running 0 19m
kubesphere-monitoring-system node-exporter-5rl89 2/2 Running 0 19m
kubesphere-monitoring-system node-exporter-67vbg 2/2 Running 0 19m
kubesphere-monitoring-system node-exporter-9cchq 2/2 Running 0 19m
kubesphere-monitoring-system node-exporter-b67r9 2/2 Running 0 19m
kubesphere-monitoring-system node-exporter-bc7f9 2/2 Running 0 19m
kubesphere-monitoring-system node-exporter-cxmmx 2/2 Running 0 19m
kubesphere-monitoring-system node-exporter-fm2zh 2/2 Running 0 19m
kubesphere-monitoring-system node-exporter-pqv4g 2/2 Running 0 19m
kubesphere-monitoring-system node-exporter-tjf7p 2/2 Running 0 19m
kubesphere-monitoring-system notification-manager-deployment-78664576cb-4j64q 2/2 Running 0 17m
kubesphere-monitoring-system notification-manager-deployment-78664576cb-hw54c 2/2 Running 0 17m
kubesphere-monitoring-system notification-manager-operator-7d44854f54-f55l4 2/2 Running 0 18m
kubesphere-monitoring-system prometheus-k8s-0 2/2 Running 1 (4m ago) 19m
kubesphere-monitoring-system prometheus-k8s-1 2/2 Running 1 (4m ago) 18m
kubesphere-monitoring-system prometheus-operator-5c5db79546-fpcs8 2/2 Running 0 19m
kubesphere-monitoring-system thanos-ruler-kubesphere-0 2/2 Running 0 18m
kubesphere-monitoring-system thanos-ruler-kubesphere-1 2/2 Running 0 18m
kubesphere-system ks-apiserver-6ff959b4cb-d4x4b 1/1 Running 0 17m
kubesphere-system ks-console-565df7f477-lptb5 1/1 Running 0 25m
kubesphere-system ks-controller-manager-6477858f96-5gdk4 1/1 Running 0 17m
kubesphere-system ks-installer-7fbc5d568f-p6kjv 1/1 Running 0 29m
kubesphere-system minio-859cb4d777-wt8jq 1/1 Running 0 27m
kubesphere-system openldap-0 1/1 Running 1 (27m ago) 27m
kubesphere-system openpitrix-import-job--1-5l8sx 0/1 Completed 0 23m
kubesphere-system redis-8f84d9fdd-l2t8l 1/1 Running 0 28m
ks-console 以 NodePort 的方式被部署,映射到节点的 30880 端口。
以默认的账户(admin + P@88w0rd)登录,可以看到集群的全部信息。下面展示了本集群的 Overview 页面:

使用 KubeSphere 部署单个应用
当我们需要部署一个应用时,应当重点思考如下内容:
- 这个应用的镜像是什么?启动命令是什么?是否有环境变量?暴露哪些端口?
- 这个应用是有状态的?还是无状态的?
- 这个应用需要哪些配置信息?
- 这个应用需要哪些存储卷?分别用于存储本应用的何种数据?
接下来以 MySQL 的部署为例进行分析。首先,在 DockerHub 上查阅官方镜像 mysql:5.7.35 的说明,可以发现启动命令为:
docker run -p 3306:3306 --name mysql-01 \
-v /mydata/mysql/log:/var/log/mysql \
-v /mydata/mysql/data:/var/lib/mysql \
-v /mydata/mysql/conf:/etc/mysql/conf.d \
-e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=root \
--restart=always \
-d mysql:5.7.35
这意味着:
- 启动命令默认为 Dockerfile 中的启动命令,无需特别关注。需要设定环境变量
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=root,暴露端口为3306; - 数据库作为一种中间件,存在需要被持久化的数据,必然以有状态应用的方式部署;
- 启动配置在
/etc/mysql/conf.d中,需要创建一个对应的 ConfigMap 并录入配置信息; - 数据被存放在
/var/lib/mysql中,需要创建一个对应的存储卷并绑定; - 如果需要持久化日志信息,也需要创建一个存储卷并挂载到
/var/log/mysql目录下。
根据以上分析,我们可以很轻易地写出对应的资源清单文件:
kind: StatefulSet
apiVersion: apps/v1
metadata:
name: his-mysql
namespace: his
labels:
app: his-mysql
annotations:
kubesphere.io/creator: admin
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: his-mysql
template:
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
app: his-mysql
annotations:
logging.kubesphere.io/logsidecar-config: '{}'
spec:
volumes:
# 创建三个存储卷。分别用于和宿主机同步时间、存储数据库数据、设定配置信息
- name: host-time
hostPath:
path: /etc/localtime
type: ''
- name: volume-nbawbw
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: mysql-pvc
- name: volume-2gsuec
configMap:
name: mysql-conf
defaultMode: 420
containers:
- name: container-hm42s8
image: 'mysql:5.7.35'
ports:
# 配置端口
- name: tcp-3306
containerPort: 3306
protocol: TCP
- name: tcp-33060
containerPort: 33060
protocol: TCP
env:
# 设定环境变量
- name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD
value: '123456'
resources:
limits:
cpu: 200m
memory: 500Mi
volumeMounts:
# 挂载三个存储卷
- name: host-time
readOnly: true
mountPath: /etc/localtime
- name: volume-nbawbw
mountPath: /var/lib/mysql
- name: volume-2gsuec
readOnly: true
mountPath: /etc/mysql/conf.d
terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log
terminationMessagePolicy: File
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
restartPolicy: Always
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst
serviceAccountName: default
serviceAccount: default
securityContext: {}
schedulerName: default-scheduler
serviceName: his-mysql-rb09 # 同时创建一个 Headless Service
podManagementPolicy: OrderedReady
updateStrategy:
type: RollingUpdate
rollingUpdate:
partition: 0
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
在 KubeSphere 中我们只需要点点鼠标就可以完成所有资源对象的创建,读者可自行把玩,此处不在展示相关截图。实际上,上述资源清单正是由 KubeSphere 根据创建结果自动生成的。 接下来,我们删除默认生成的 Headless Service,然后手动创建一个 NodePort 类型的 Service,使得 MySQL 实例可以被子网内节点访问。如果一切顺利,应该可以看到:
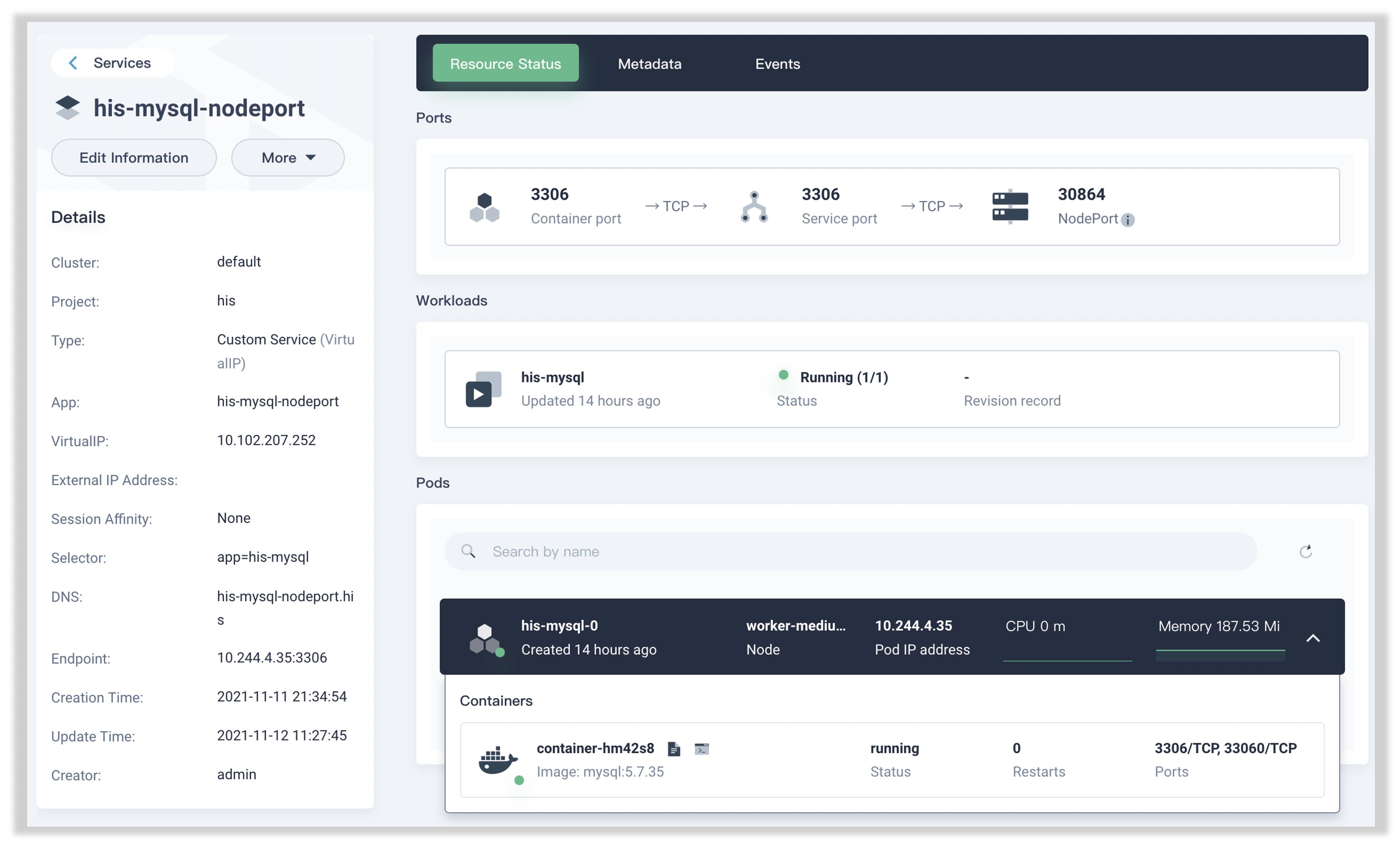
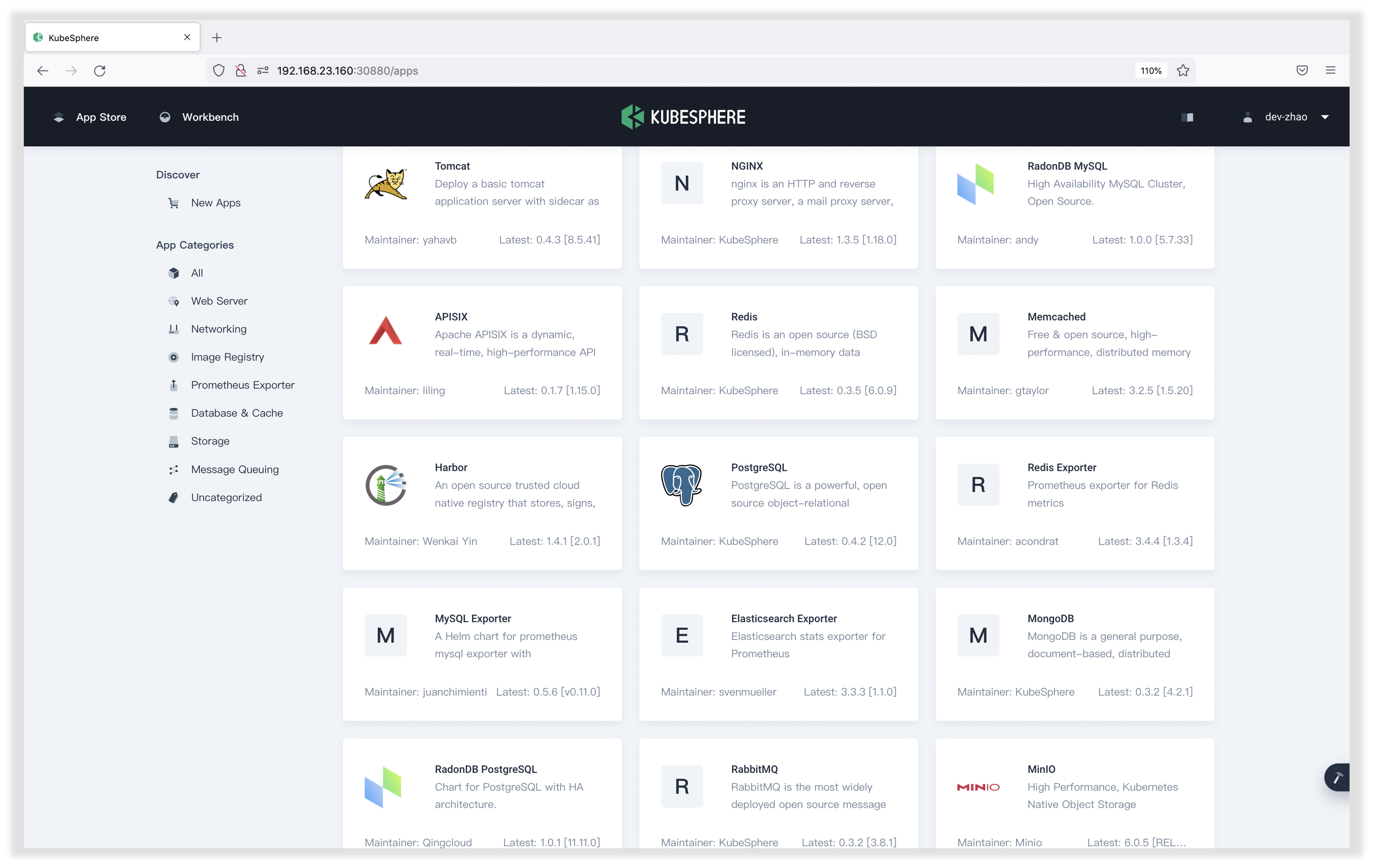
如果还想再轻松一些,我们还可以直接在 KubeSphere 提供的 App Store 中点击一键式部署 3,这样我们连 Volume 和 ConfigMap 的创建与挂载都不用操作了。
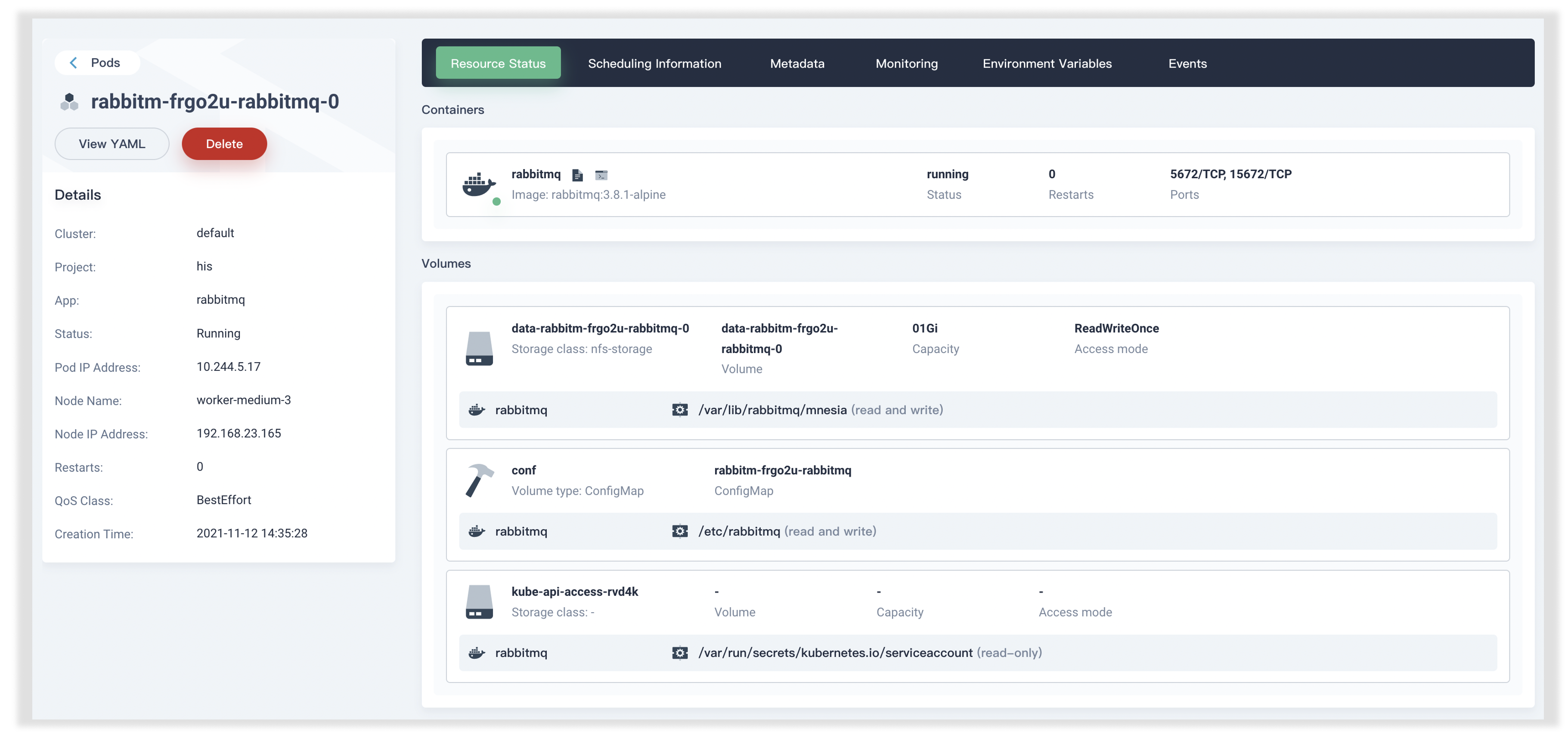
我们在 App Store 中一键式部署 RabbitMQ,可以发现 Volume 和 ConfigMap 都已自动为我们创建:
总结
本文主要介绍了 KubeSphere 的安装与基本使用。 实际上,KubeSphere 的强大之处在于它可以大大简化复杂项目的部署,我将在后续文章中向读者展示这一点。
转载申请
本作品采用 知识共享署名 4.0 国际许可协议 进行许可,转载时请注明原文链接。您必须给出适当的署名,并标明是否对本文作了修改。
-
KubeSphere 官方网站为 https://kubesphere.com.cn/。 ↩︎
-
https://kubesphere.com.cn/docs/quick-start/minimal-kubesphere-on-k8s/ ↩︎
-
除了 App Store,还可以在 KubeSphere 中添加镜像仓库(如 bitnami 官方镜像仓库)通过 Helm 一键式部署。这大大丰富了可一键式部署的镜像数量。 ↩︎